5 Common Injuries Sustained in Truck Accidents
Key Takeaways: Truck accidents often cause severe injuries like spinal cord injuries, traumatic brain injury, broken bones, internal injuries, and...
3 min read
Juan Carlos : 3/21/22 12:00 AM
Getting a divorce is seldom easy. Apart from emotional strain and social stigma, you’re also likely to experience financial difficulties. Whether it be legal fees, giving away belongings or having to survive on a single income, divorce can create many financial hardships. In cases where the marriage lasted several years or the couple had children together, one of the spouses may be eligible for alimony and/or child support.
If you’re in the process of getting a divorce, it’s important to understand the differences between alimony and child support and whether you may be entitled to receiving it or obligated to pay it.
In general, spousal support, sometimes referred to as alimony or spousal maintenance, is money paid by one spouse to financially support the other after a divorce is granted.
Child support is paid to financially support a child or children resulting from the marriage. Child support should only be spent on child-related expenses, like food, clothing, childcare, medical care, etc.
According to Georgia law, spousal support can be either rehabilitative or permanent and is usually granted after a long-term marriage ends.
Rehabilitative alimony is short-term maintenance which is supposed to help the receiving ex-spouse get on their feet. This type of alimony is usually awarded to spouses who were homemakers and raised children. Typically, it’s the ex-husband who ends up paying rehabilitative alimony to his ex-wife but it’s possible for the roles to be reversed.
Permanent alimony is paid for a lengthy period of time, often until the death or remarriage of the receiving party. It is typically granted when one of the parties is unable to work due to illness or disability.
Alimony can only be granted if the receiving party requests it during divorce proceedings.
Unless the couple can agree on a fixed amount, a judge awarding the alimony will make their decision based on the following factors:
In Georgia, alimony is typically terminated when the receiving spouse either dies or remarries. In all other cases, the paying party will have to file a motion with the court to modify alimony. Typically, this happens when the paying ex-spouse loses their job or experiences other life-altering hardships, like illness or disability.
If the receiving ex-spouse suffers financial hardships, they can request higher alimony payments. Both scenarios are likely to be dismissed by the judge if both parties surrendered their rights to alimony modification during the divorce proceedings.
If you and your ex-spouse had children together and you now have custody of them, meaning the children stay with you more than half the time, you are likely entitled to child support. Georgia courts and attorneys take into consideration both parents’ incomes to make the determination as fair as possible for the children and each parent.
Typically, the courts use a simple calculation based on the combined gross income of both parents, the number of children they have together and each parent’s ratio of the combined income.
Under Georgia law, if you get a divorce and are ordered to pay child support, your original amount can only be changed if you ask the court to modify the agreement. If you’ve lost your job or endured other financial hardships, you can request that child support payments be lowered.
Child support payments are typically canceled or modified once your child turns 18 years old or if custody and parenting arrangements change. In the latter situation, you’ll still have to petition the court to officially terminate your financial obligations to your ex-spouse. Child support may continue past the age of 18 if the child has a disability or condition that warrants continued financial support.
As a custodial parent, you can petition the court to increase your ex-spouse’s child support obligation if you can prove their financial situation has significantly improved or your child’s financial needs have changed.
If you’re not sure how to handle your divorce in terms of alimony or child support, talk to an experienced family attorney, like Isaac F. Cotto, who’s both knowledgeable and compassionate when working with his clients.
Don’t hesitate to call us at (770) 817-7581 for a consultation.
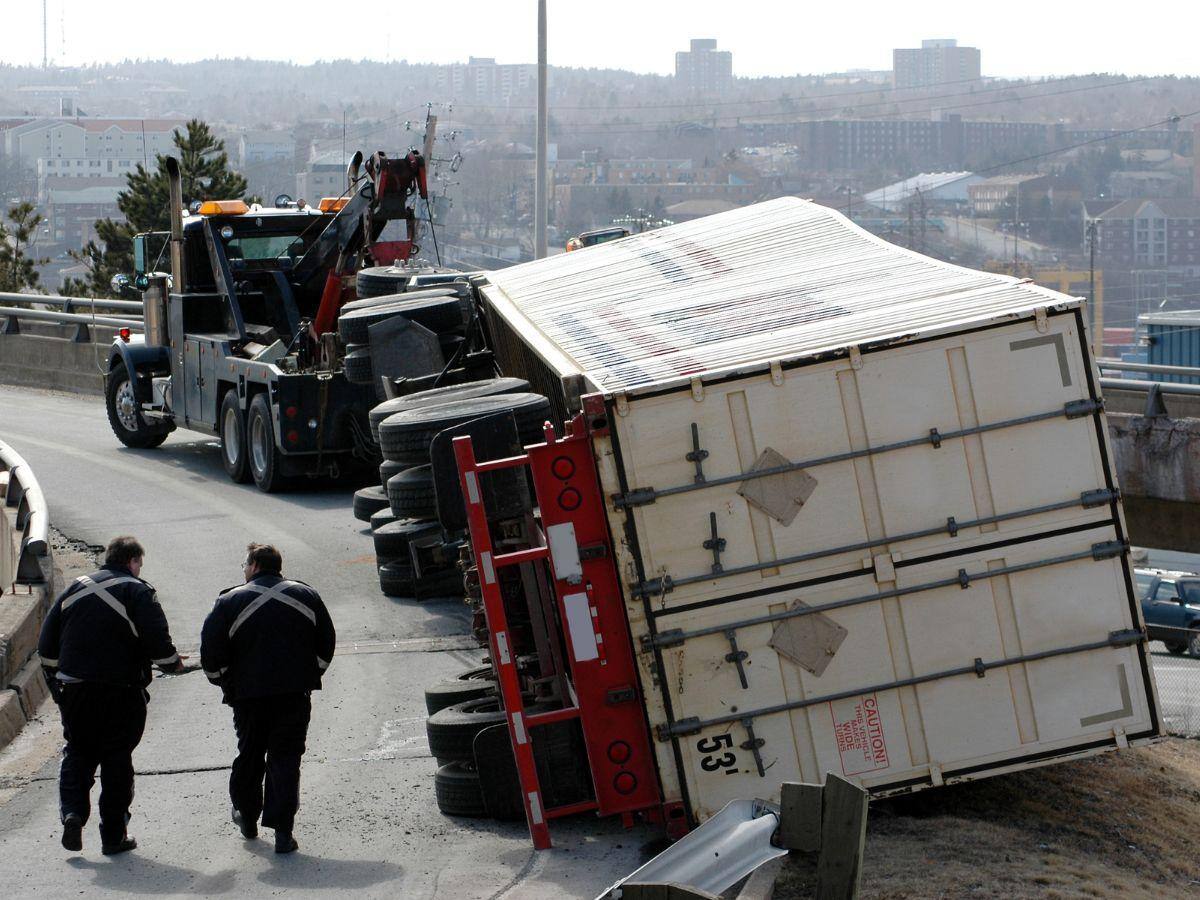

Key Takeaways: Truck accidents often cause severe injuries like spinal cord injuries, traumatic brain injury, broken bones, internal injuries, and...

3 min read
Political asylum is occasionally granted to applicants in the United States, but it’s often difficult to obtain due to inconsistent interpretation...
3 min read
Según la Comisión para la Igualdad de Oportunidades en el Empleo, los empleadores pueden imponer vacunas a sus empleados siempre que tengan en...